About Access Control System
2015-08-14
RFID reader restarts again or powerlight is dim when door opens.

1.Check if both reader and electric lockare sharing the same current
2.Do not share the current with other unitsor equipments to avoid interference.
No action from the lock when the cardis sensed.

1.Check the power supply of the unit and ifthe POWER (red) light of the panel is on.
2.RFID the card and check OK (green) light.If it is on, check electric lock’s power supply and connections.
3.RFID the card and check DENY (yellow)light. It is on when unregistered card is sensed
4.Continuous proximity. Remove the car fromthe RFID area and then try again.
5.Check door open mode (set as RFID mode).
6.Wrong format of card or malfunction ofcard if both OK and DENY lights do not respond at all.
Access system password is entered butunable to enter into various functional selection of the setting mode

1.Incomplete input of system password,please check if correct format “*XXXX #” (XXXX as system password) has been entered as required in manual.
2.System password has been changed. Inquirereader’s parameterto get the password if it is networking reader. Contact your nearby agent orreturn to the manufacturer if it is stand-alone reader.
3.Bad wire arrangement which might causeshort circuit of the PC board. Check the power supply and the control wires inorder to avoid the wires pressing on the PC board causing bad contact, shortcircuit and interference.
4.Strong interference from other equipmentsor same type unit caused the new unit is unable to enter Setting Mode or slowresponse from the keypad. Move the new unit to other place to test again
How to stop anti-damage activation or duress alarm activation?

1.RFID the card and open the door asregular basis again to turn it off.
2.Check the activation of the alarm forsecurity purposes.
3.When the alarm is still on and thenetwork software shows the unit is being tampered which means the anti-tamperswitch is not closely mounted onto the wall.
AbnormalRFID response from the reader (wrong Beep sound).

1.Check if any unregistered cards nearby.
2.Do not share the current with otherreaders or equipments to avoid interference.
3.Increase the distance of the readers toavoid interference with each other if there are more than one reader nearby.
Readeris unable to read card, no response from the keypad and unable to enter settingmode.

1.Check the power supply or restart itagain.
2.Check if diodes are loaded as instructedin the manual if the electric lock is functional after restarting.
3.Please contact your nearest agent orreturn to the manufacturer for testing if all of the above solutions are unableto solve the problem.
What is Access Control System?
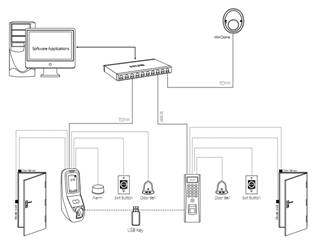
Access control system refers to thepractice of restricting entrance to a property, a building, or a room toauthorized persons. Physical access control can be achieved by a human (aguard, bouncer, or receptionist), through mechanical means such as locks andkeys, or through technological means such as access control systems.
Physical access control is a matter of who,where, and when. An access control system determines who is allowed to enter orexit, where they are allowed to exit or enter, and when they are allowed toenter or exit.
Historically this was partiallyaccomplished through keys and locks. When a door is locked only someone with akey can enter through the door depending on how the lock is configured. However. . .
Mechanical locks and keys do not allowrestriction of the key holder to specific times or dates.
Mechanical locks and keys do not providerecords of the key used on any specific door and the keys can be easily copiedor transferred to an unauthorized person.
When a mechanical key is lost or the keyholder is no longer authorized to use the protected area, the locks must bere-keyed.
Electronic access control uses computers tosolve the limitations of mechanical locks and keys. A wide range of credentialscan be used to replace mechanical keys.
The electronic access control system grantsaccess based on the credential presented.
When access is granted, the door isunlocked for a predetermined time and the transaction is recorded.
When access is refused, the door remainslocked and the attempted access is recorded.
The system will also monitor the door and alarmif the door is forced open or held open too long after being unlocked.
How the Access Control System works?
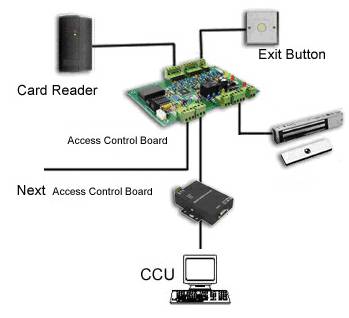
When a credential (card, password,biometric etc.) is presented to a reader, the reader sends the credential’s information, usually a number, toa control panel / processor. The control panel compares the credential's numberto an access control list, grants or denies the presented request, and sends atransaction log to a database. When access is denied based on the accesscontrol list, the door remains locked. If there is a match between thecredential and the access control list, the control panel operates a relay thatin turn unlocks the door. The control panel also ignores a door open signal toprevent an alarm. Often the reader provides feedback, such as a flashing redLED for an access denied and a flashing green LED for an access granted.
The above description illustrates a singlefactor transaction. Credentials can be passed around, thus subverting theaccess control list. For example, Alice has access rights to the server roombut Bob does not. Alice either gives Bob her credential or Bob takes it; he nowhas access to the server room. To prevent this, two-factor authentication canbe used. In a two factor transaction, the presented credential and a secondfactor are needed for access to be granted; another factor can be a PIN, asecond credential, operator intervention, or a biometric input.
There are three types (factors) ofauthenticating information:
something the user knows, e.g. a password,pass-phrase or PIN
something the user has, such as smart card
something the user is, such as fingerprint,verified by biometric measurement
Passwords are a common means of verifying auser's identity before access is given to information systems. In addition, afourth factor of authentication is now recognized: someone you know, whereanother person who knows you can provide a human element of authentication insituations where systems have been set up to allow for such scenarios. Forexample, a user may have their password, but have forgotten their smart card.In such a scenario, if the user is known to designated cohorts, the cohorts mayprovide their smart card and password in combination with the extant factor ofthe user in question and thus provide two factors for the user with missingcredential, and three factors overall to allow access.











 Add: Room 417, Sun\'gang Building, No. 23, Baogang
Add: Room 417, Sun\'gang Building, No. 23, Baogang Tel: +86-755-8637 7711
Tel: +86-755-8637 7711  Fax: +86-755-8276 2979
Fax: +86-755-8276 2979  Website:
Website: 





